Page 27 - El Modelo de Regresión Lineal
P. 27
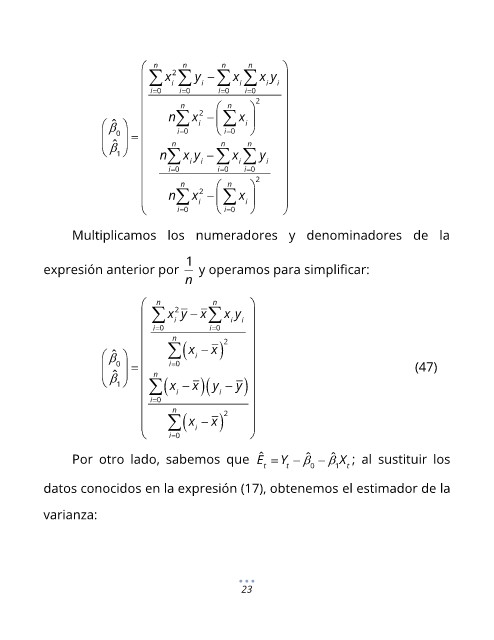
n 2 n n n
i
x i y − x i x y i
i
i= 0 i= 0 i= 0 i= 0
n n 2
2
n x − x i
ˆ
= i i
0 = i 0 = 0
ˆ
n
1
i
n x y − n x n y
i= 0 i i= 0 i i= 0 i
n n 2
n x − x i
2
i
i = 0 i = 0
Multiplicamos los numeradores y denominadores de la
1
expresión anterior por y operamos para simplificar:
n
n 2 n
x y − x x y i
i
i
i = 0 i = 0
n ( x ) 2
x −
ˆ
i
ˆ 0 = n i= 0 (47)
1
( x − x )( y − y )
i i
i= 0 n
( x − x ) 2
i
i= 0
ˆ
Por otro lado, sabemos que E = Y − ˆ − ˆ X ; al sustituir los
t t 0 1 t
datos conocidos en la expresión (17), obtenemos el estimador de la
varianza:
23