Page 15 - La matriz inversa
P. 15
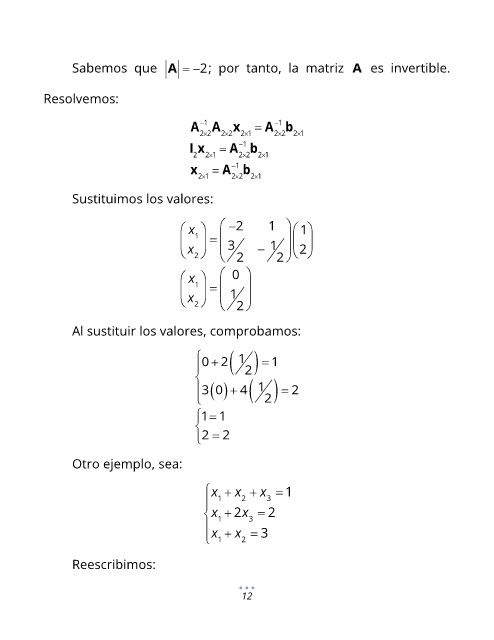
Sabemos que A = − 2; por tanto, la matriz A es invertible.
Resolvemos:
A A x 2 1 = A b
−
1
−
1
2 2
2 2
2 2 2 1
1
I x = A b
−
2 2 1 2 2 2 1
1
x 2 1 = A b
−
2 2 2 1
Sustituimos los valores:
x 2 1 − 1
1 = 3 1
x 2 2 − 2 2
x 0
1 = 1
x 2 2
Al sustituir los valores, comprobamos:
0 2 ( ) = 1
1
+
2
1
3 0 + ( ) 4 ( ) = 2
2
1 1
=
2 = 2
Otro ejemplo, sea:
x + x + x = 1
1 2 3
x + 1 2x = 3 2
3
x + 1 x = 2
Reescribimos:
12